Codling Moth: Larval Emergence
 This Week: We have passed the window for use of pheromone trapping to capture the first CM adult for on farm biofix in the Hudson Valley and we are too late to effectively control 1st generation CM through mating disruption. The first adult flight was observed in Clintondale on 11 May, Highland on 12 May and Peru near the lake on 18 May. Trap capture signals the adult biofix and model prediction for larval emergence for these sites. The use of models found on NEWA combined with your orchard site pheromone traps is the best way to time directed applications for this pest. In the mid-Hudson Valley, larva emergence will occur during the latter part of this week (Tuesday May 30th). Given the rain events forecast for this week the application window is for the 1st and 2nd of June.
This Week: We have passed the window for use of pheromone trapping to capture the first CM adult for on farm biofix in the Hudson Valley and we are too late to effectively control 1st generation CM through mating disruption. The first adult flight was observed in Clintondale on 11 May, Highland on 12 May and Peru near the lake on 18 May. Trap capture signals the adult biofix and model prediction for larval emergence for these sites. The use of models found on NEWA combined with your orchard site pheromone traps is the best way to time directed applications for this pest. In the mid-Hudson Valley, larva emergence will occur during the latter part of this week (Tuesday May 30th). Given the rain events forecast for this week the application window is for the 1st and 2nd of June.
A number of products are available for use in New York State. In blocks of high fruit infestation from codling moth in 2017, a possible cause may have been the use of materials ineffective against the worm during the three generation emergence periods of the larval stage, most notably the 3rd generation in September. The use of Actara (thiamethoxam) for plum curculio at PF, 1st or 2nd cover will not have provided commercial control of the 1st generation CM. The possibility of frequently used insecticides slipping is also a possibility.
Best application date appears to be Wednesday or Thursday of this week (June 1st or 2nd, 2017).

NOAA forecast for Memorial Day week.
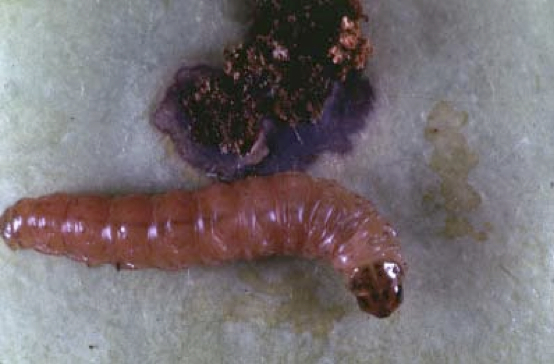
Introduction: It can be argued that of the internal worm complex, the codling moth has historically been the greatest threat to tree fruit. This insect continues to re-emerge as a primary pest of apple throughout the world. During the 2016 harvest we observed very high levels of fruit infestation in Hudson Valley apple, ranging from 2% to 40% injury in commercial production.
The insect is now overwintering as full-grown larvae, residing within a silken cocoons, tucked under inaccessible bark scales, in soil or hidden in the leaves and debris around the base of trees. The larvae will pupate and emerge from their cocoon early in the spring as an adult moths. The range of first flight begins from ate April to early May this season due to a cool spring, with first hatch beginning late May to early June.
Conventional material options are listed in the Cornell Guidelines.


An additional option is to apply a granulosis virus formulation at 200-250 DD 50°F. High moth pressure requires 2-3 sprays for the first generation, but in lower pressure orchards (with counts of less than 5 moths per trap per week), you can control CM with a single spray timed at 350 DD 50°F.Codling moth granulosis virus. Formulations include Cyd-X, Cyd-X HP, Madex HP by Certis; Carpovirusine by Arysta LifeScience. Cyd-X 0.06SC is applied @ 0.25-0.4 qt/acre and Carpovirusine 0.99SC @ 0.25-0.4 qt/acre.
Codling Moth Granulosis Virus contains an insecticidal baculovirus, Cydia pomonella granulovirus, which is specific to the larval form of the codling moth, and is registered for use in apples, pears, and (Cyd-X only) plums. This biological insecticide must be ingested in order to be effective, after which the viral occlusion bodies dissolve in the larval midgut and release infectious virions. These enter the cells lining the digestive tract, where they replicate; eventually, the other tissues are infected and the larva stops feeding and eventually (within 3-7 days) dies. After death, the larva disintegrates, releasing billions of new occlusion bodies, which may infect other codling moth larvae upon ingestion. No adverse effect to fish, wildlife or beneficial organisms has been observed; it has a low bee-poisoning hazard and .

Chemical class, activity and timing of in
secticides used for CM control.
(Wise, MSU)
An additional option is to apply a granulosis virus formulation at 200-250 DD 50°F. High moth pressure requires 2-3 sprays for the first generation, but in lower pressure orchards (with counts of less than 5 moths per trap per week), you can control CM with a single spray timed at 350 DD 50°F.Codling moth granulosis virus. Formulations include Cyd-X, Cyd-X HP, Madex HP by Certis; Carpovirusine by Arysta LifeScience. Cyd-X 0.06SC is applied @ 0.25-0.4 qt/acre and Carpovirusine 0.99SC @ 0.25-0.4 qt/acre.
Codling Moth Granulosis Virus contains an insecticidal baculovirus, Cydia pomonella granulovirus, which is specific to the larval form of the codling moth, and is registered for use in apples, pears, and (Cyd-X only) plums. This biological insecticide must be ingested in order to be effective, after which the viral occlusion bodies dissolve in the larval midgut and release infectious virions. These enter the cells lining the digestive tract, where they replicate; eventually, the other tissues are infected and the larva stops feeding and eventually (within 3-7 days) dies. After death, the larva disintegrates, releasing billions of new occlusion bodies, which may infect other codling moth larvae upon ingestion. No adverse effect to fish, wildlife or beneficial organisms has been observed; it has a low bee-poisoning hazard.
Insecticide Resistance Development in Codling Moth:
The organophosphate class of insecticides, including Guthion (azinphos-methyl) and Imidan (phosmet) have been used since the 1960’s, for over 50 years, to manage the codling moth. The development of resistance by codling moth to Imidan is likely if its reoccurring use has been for Plum Curculio and or OBLR management during mid-summer. Consistent use during the past ten years or more increasing resistance potential. Those specific timings would provide some level of control of CM while providing various rates of residual exposure. Low rates of residual increase the selection for resistance during the early and mid-summer generations of the pest. A scenario, such as the switch from Guthion to Imidan in season long program use would affect the same target site (nerve receptor sites for ACh, acetylcholinesterase) within the insect to contribute to resistance.
In the Hudson Valley to date I don’t believe resistant strains are widespread, even though we are hearing of increasing reports of CM damage to tree fruit. The broad availability and use of insecticides that include the different IRAC classes of active ingredients for plum curculio from PF to 2nd cover and mid-summer management of OBLR, would reduce region-wide resistance of CM to any one specific insecticide class. We have seen the use of these materials to include Avaunt, Exirel, Calypso, Carbaryl, pre-mixes including pyrethroids or pyrethroids alone. Insecticides of various classes for the overwintering OBLR used at PF would likely impact CM to a lesser degree when used at petal fall timing.
There haven’t been recent studies to detect phosmet resistance to CM in NY that I’m aware of. In Michigan, a study in 2008 detected a 7-8 fold level of resistance in orchard site specific CM populations to codling moth
Insecticide rotation: I would suggest the use of specific materials for CM be employed during 1st-2nd cover and again in mid-July, when model predictions for larva emergence are called for AND in orchards with reoccurring fruit injury from CM. The use of Assail to manage apple maggot during 2nd generation CM larval emergence has been a good option, as it’s been shown to be one of the better materials against both CM & AM. The use of Delegate, Altacor at 1st – 2nd cover would reduce the resistance potential while picking up a few lingering overwintering OBLR. Mating disruption and granulosis virus are also good choices in conventional and organic production systems.
Remember to rotate classes for EACH GENERATION and not each spray during a generation, to reduce the potential for insecticide resistance. So for example: Two applications of Altacor for the first generation in Highland beginning June 1st